Customer Support
+919871596367
Connect With Email
info@prakharmedics.com

Blog Post
Surgical Dressings


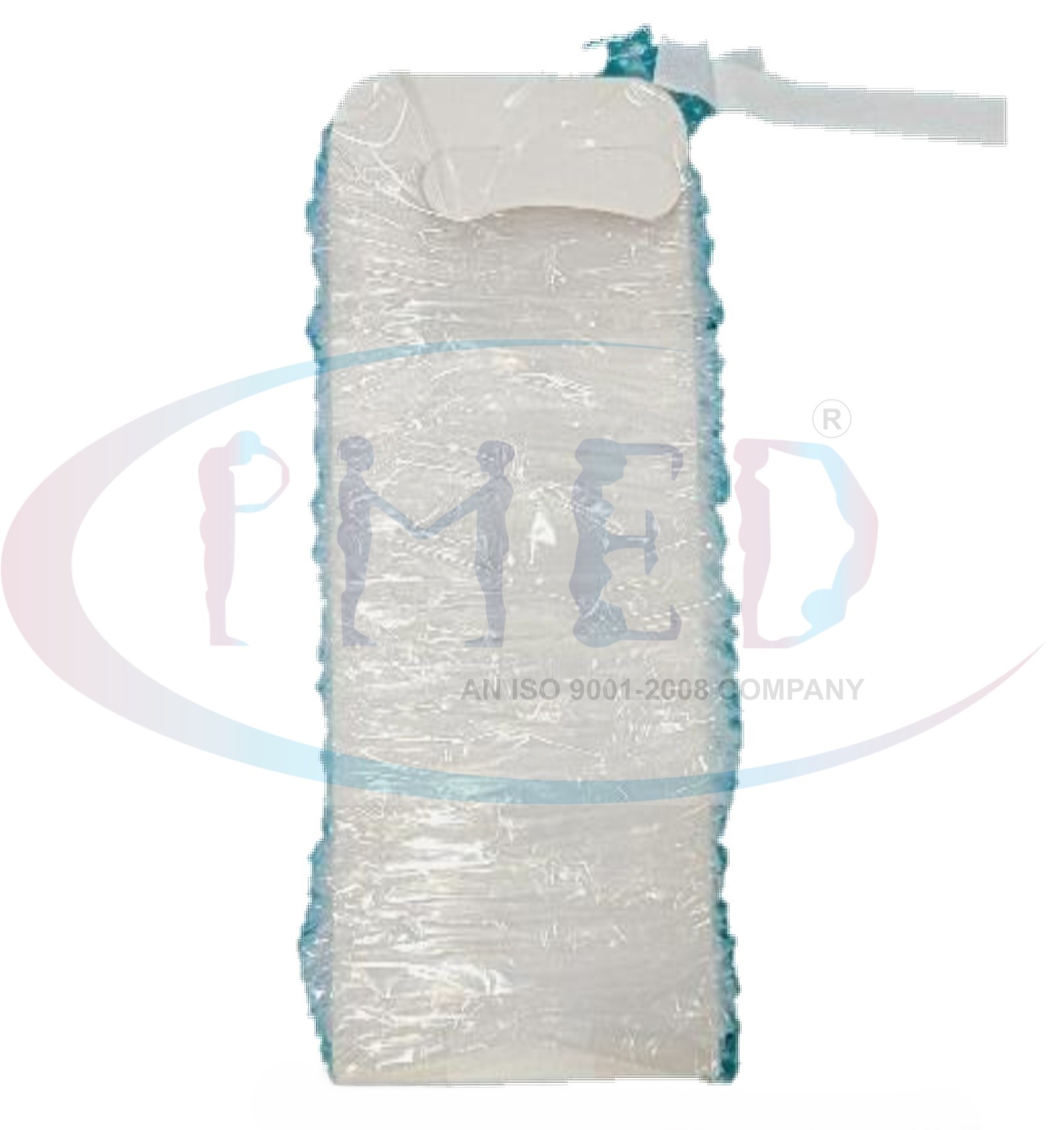
1. Gauze Dressings
Description: Made from woven or non-woven fabric, gauze dressings are used to cover and protect wounds. They are highly absorbent and come in various forms such as pads, sponges, and rolls. Usage: Commonly used for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate (drainage), as primary or secondary dressings.
2. Transparent Film Dressings
Description: These are thin, transparent, adhesive dressings that allow the wound to be monitored without removal. They are impermeable to bacteria and water but allow oxygen and moisture vapor to pass through. Usage: Ideal for superficial wounds, IV sites, and areas requiring visual inspection. Not suitable for heavily exuding wounds.
3. Hydrocolloid Dressings
Description: Composed of a gel-forming agent like carboxymethylcellulose, hydrocolloid dressings adhere to the skin and form a gel in contact with wound exudate. They maintain a moist environment that promotes healing. Usage: Suitable for low to moderate exuding wounds, pressure ulcers, and burns. They provide a barrier against bacteria and other contaminants.
4. Hydrogel Dressings
Description: Hydrogels are water- or glycerin-based dressings that keep the wound moist, promoting cellular migration and aiding in debridement. Usage: Best for dry or necrotic wounds, pressure ulcers, and radiation burns. They are soothing and can help reduce pain.
5. Foam Dressings
Description: Made of polyurethane, foam dressings are soft, highly absorbent, and provide thermal insulation. They maintain a moist wound environment while protecting the wound from external contaminants. Usage: Used for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, including pressure ulcers, leg ulcers, and surgical wounds.
6. Alginate Dressings
Description: Derived from seaweed, alginate dressings are highly absorbent and transform into a gel when they come into contact with wound exudate. They can absorb significant amounts of fluid. Usage: Appropriate for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, including pressure ulcers, venous ulcers, and infected wounds.
7. Composite Dressings
Description: Composite dressings combine multiple layers, each serving a different function, such as absorption, protection, and adhesion. They often include a non-adherent layer to prevent sticking to the wound. Usage: Suitable for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, providing a combination of benefits from different dressing types.
8. Antimicrobial Dressings
Description: These dressings are impregnated with antimicrobial agents like silver, iodine, or honey, which help reduce bacterial load and prevent infection. Usage: Used for infected wounds or wounds at high risk of infection.
9. Hydrofiber Dressings
Description: Made of carboxymethylcellulose fibers, hydrofiber dressings are highly absorbent and form a gel upon contact with wound exudate, which helps maintain a moist wound environment. Usage: Ideal for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, such as leg ulcers and surgical wounds.
10. Collagen Dressings
Description: Collagen dressings, derived from animal sources, provide a scaffold for new tissue growth and promote wound healing. Usage: Suitable for partial- and full-thickness wounds, including pressure ulcers, diabetic ulcers, and surgical wounds.








0 Comments