Customer Support
+919871596367
Connect With Email
info@prakharmedics.com

Blog Post
Contagious Disease protection

.jpeg)
Contagious disease protection encompasses various strategies, practices, and products aimed at preventing the spread of infectious diseases. These measures are critical in healthcare settings, public spaces, and personal environments to control and mitigate the transmission of pathogens. Here's a detailed description of the key components and methods used in contagious disease protection:
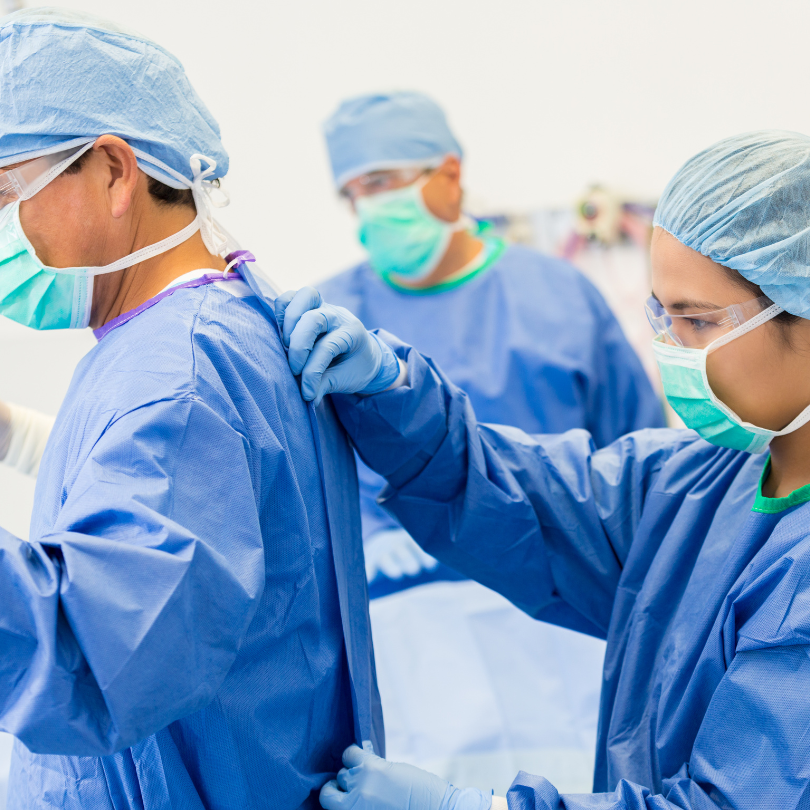
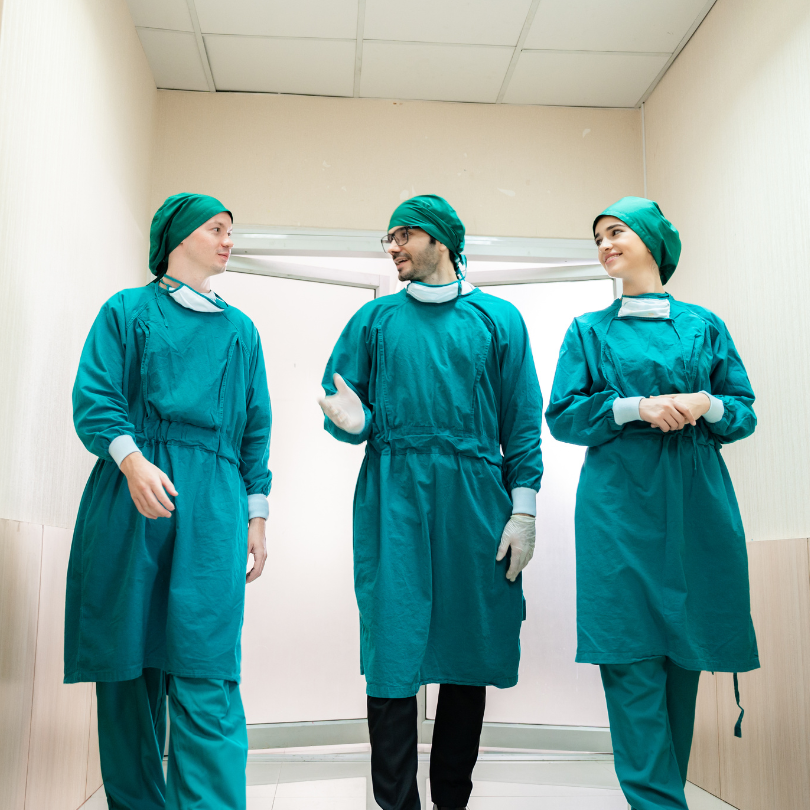
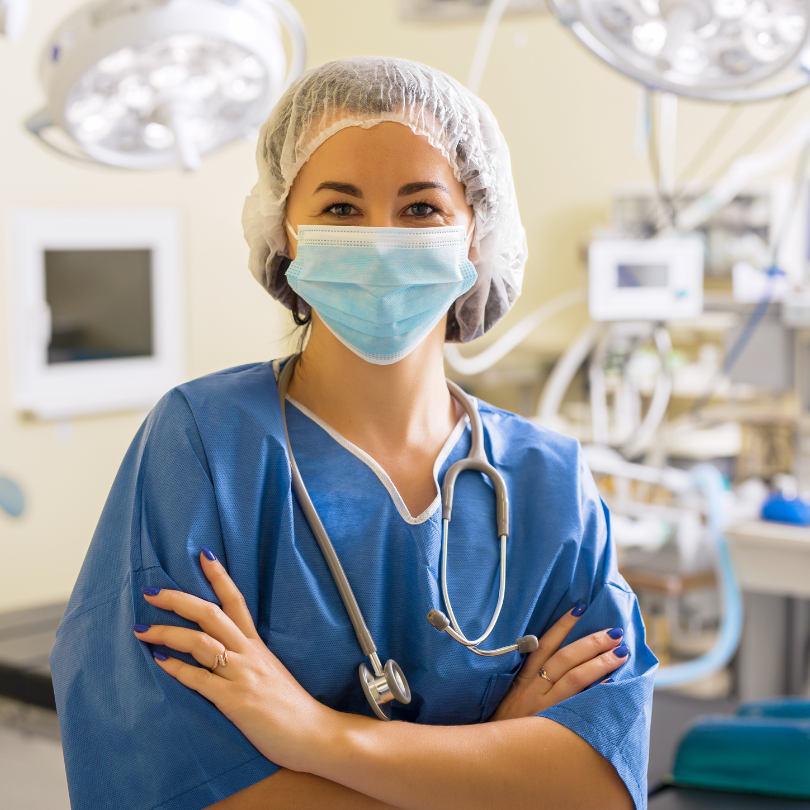
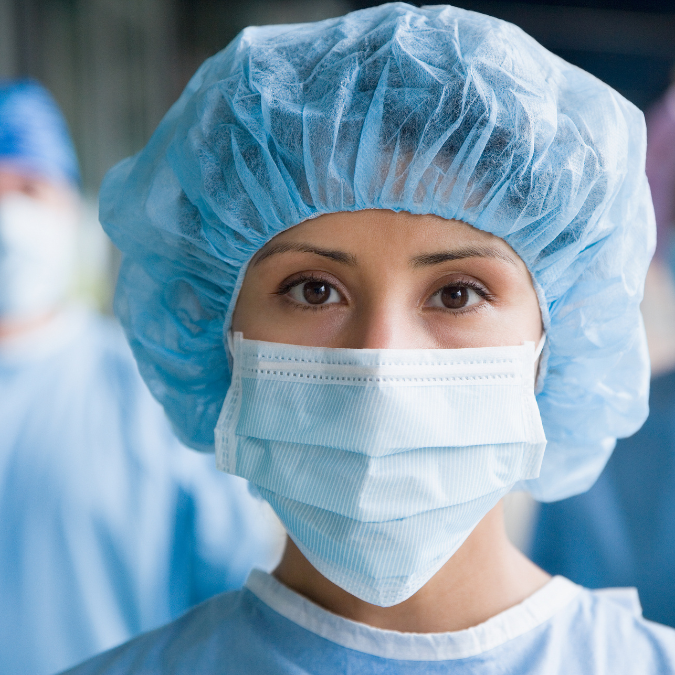
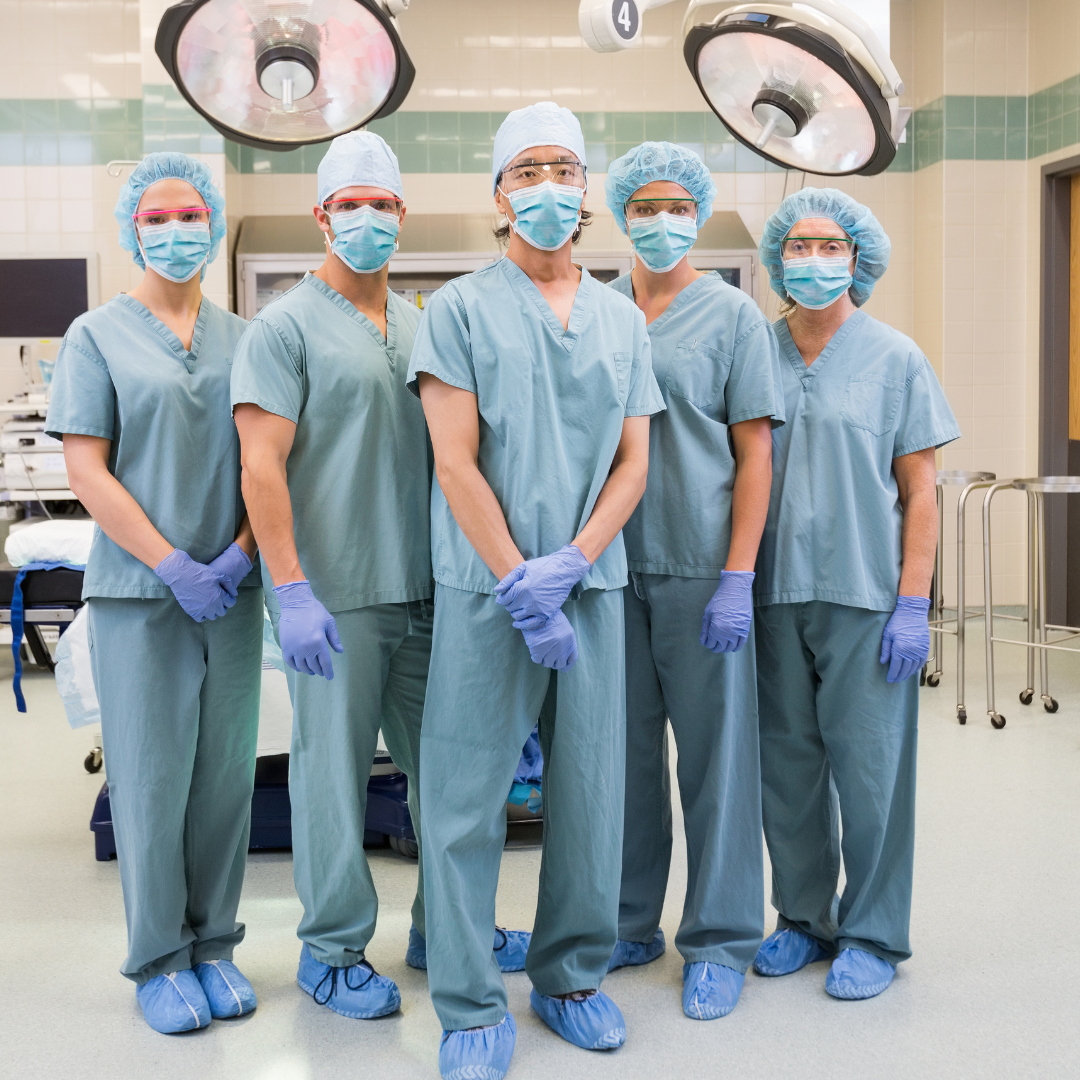
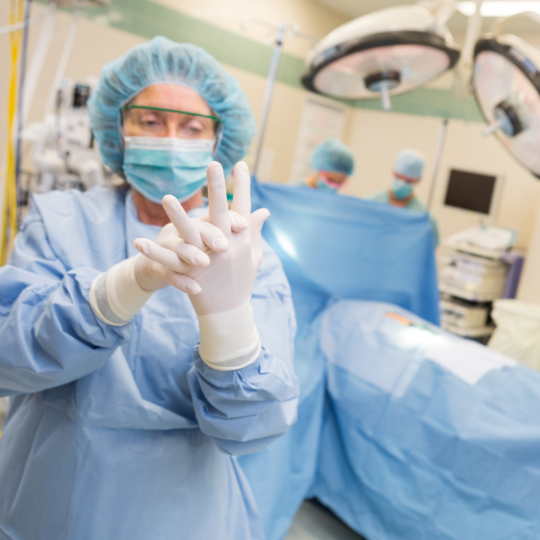
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Masks:
- Description: Face masks, including surgical masks and N95 respirators, are worn to filter out airborne particles and prevent the inhalation of pathogens.
- Usage: Essential in preventing respiratory infections like influenza, COVID-19, and tuberculosis.
Gloves:
- Description: Disposable gloves made of latex, nitrile, or vinyl used to prevent the spread of pathogens through direct contact.
- Usage: Worn when handling potentially contaminated materials or caring for infected individuals.
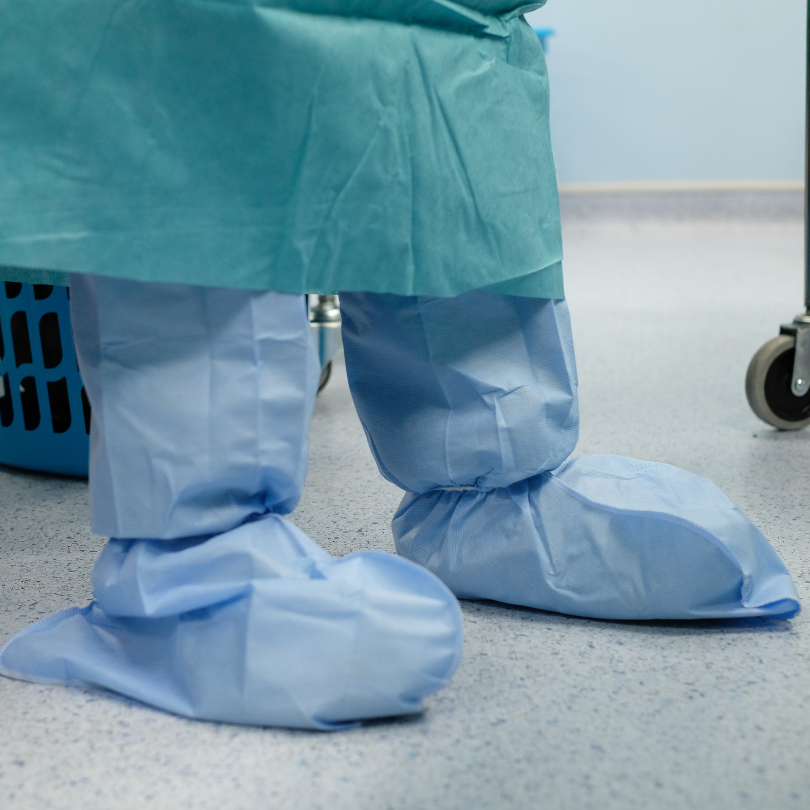
Gowns and Aprons:
- Description: Protective clothing to shield the body and clothing from infectious agents.
- Usage: Used in healthcare settings during surgical procedures, patient care, and when dealing with bodily fluids.
Face Shields and Goggles:
- Description: Eye and face protection to prevent exposure to infectious droplets.
- Usage: Used alongside masks to provide full facial protection, particularly in procedures that generate aerosols.
2. Hygiene Practices:
Hand Hygiene:
- Description: Regular hand washing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers to eliminate pathogens.
- Usage: Critical in preventing the spread of infections through touch.
Respiratory Hygiene:
- Description: Practices such as covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing.
- Usage: Reduces the dissemination of respiratory droplets.
3. Vaccination:
- Description: Administration of vaccines to stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens.
- Usage: Prevents outbreaks of diseases like measles, influenza, hepatitis, and COVID-19 by building herd immunity.
4. Environmental Controls:
Surface Disinfection:
- Description: Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces with EPA-approved disinfectants.
- Usage: Prevents the spread of pathogens on frequently touched surfaces like doorknobs, light switches, and medical equipment.
Air Filtration and Ventilation:
- Description: Use of HEPA filters, air purifiers, and proper ventilation systems to reduce airborne pathogens.
- Usage: Essential in enclosed spaces to minimize the risk of airborne transmission.
5. Isolation and Quarantine:
- Description: Separating individuals who are infected (isolation) or potentially exposed (quarantine) to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Usage: Implemented during outbreaks to control the spread of diseases like COVID-19, Ebola, and tuberculosis.
6. Screening and Surveillance:
- Description: Monitoring and testing for early detection of infectious diseases.
- Usage: Includes temperature checks, symptom screening, and diagnostic testing to identify and isolate cases promptly.
7. Antimicrobial Stewardship:
- Description: Appropriate use of antibiotics and antivirals to prevent the development of resistant strains of pathogens.
- Usage: Ensures that medications are used effectively and only when necessary, reducing the spread of resistant infections.
8. Education and Training:
- Description: Providing information and training to healthcare workers, patients, and the public on infection prevention practices.
- Usage: Enhances compliance with protective measures and promotes community-wide health.
9. Barriers and Physical Distancing:
- Description: Use of physical barriers like plexiglass and maintaining safe distances to reduce the spread of infectious agents.
- Usage: Implemented in workplaces, schools, and public areas to reduce close contact and transmission.
10. Waste Management:
- Description: Proper disposal of medical and hazardous waste to prevent contamination and spread of pathogens.
- Usage: Involves the use of designated containers, safe disposal practices, and regular sanitation protocols.
These components of contagious disease protection work together to create a comprehensive approach to infection control, reducing the risk of transmission and protecting public health. Each element is crucial in different settings and situations, from personal hygiene practices to institutional policies and global health strategies.








0 Comments